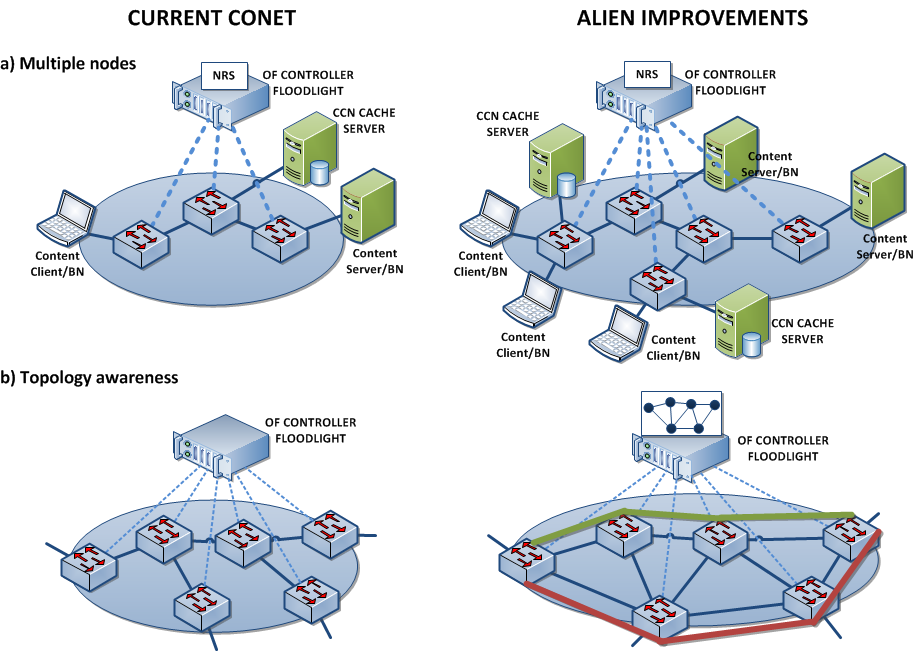
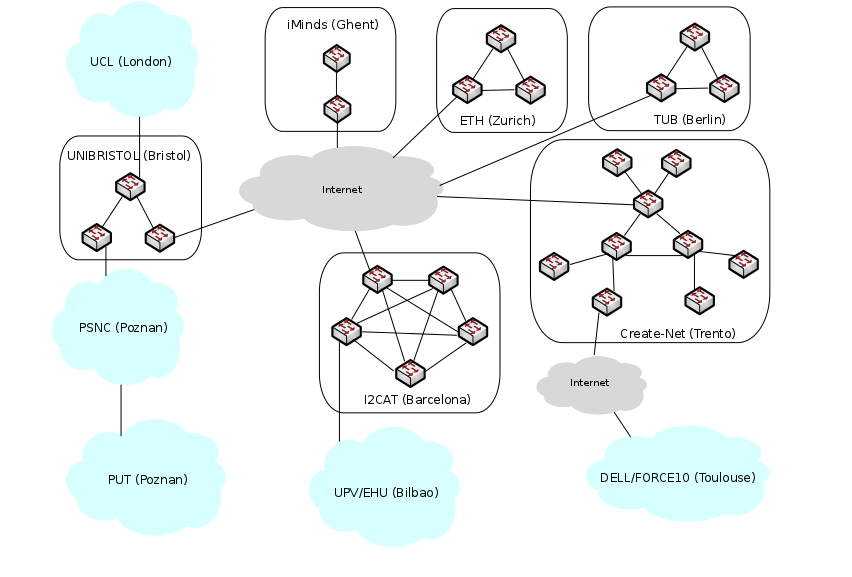
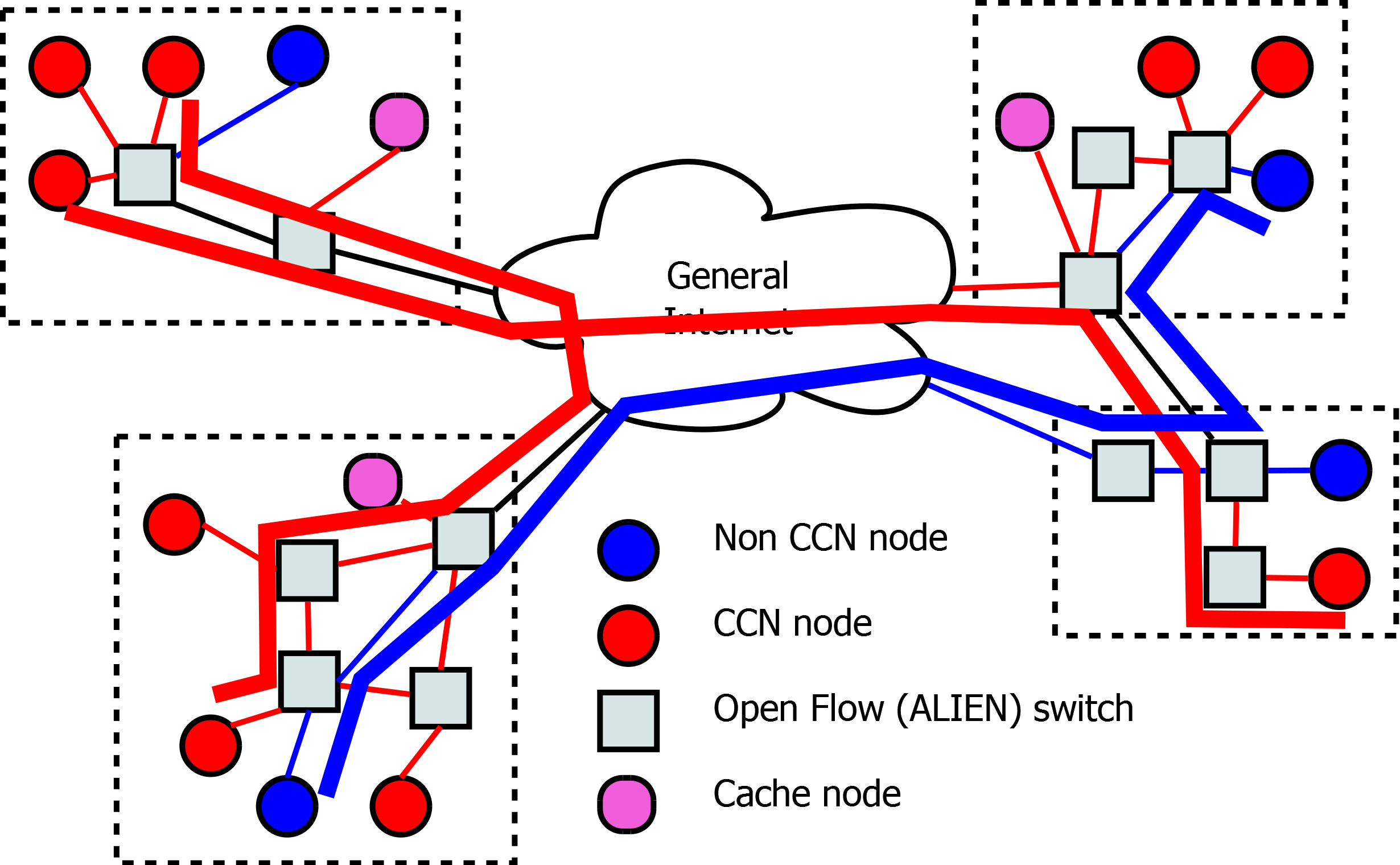
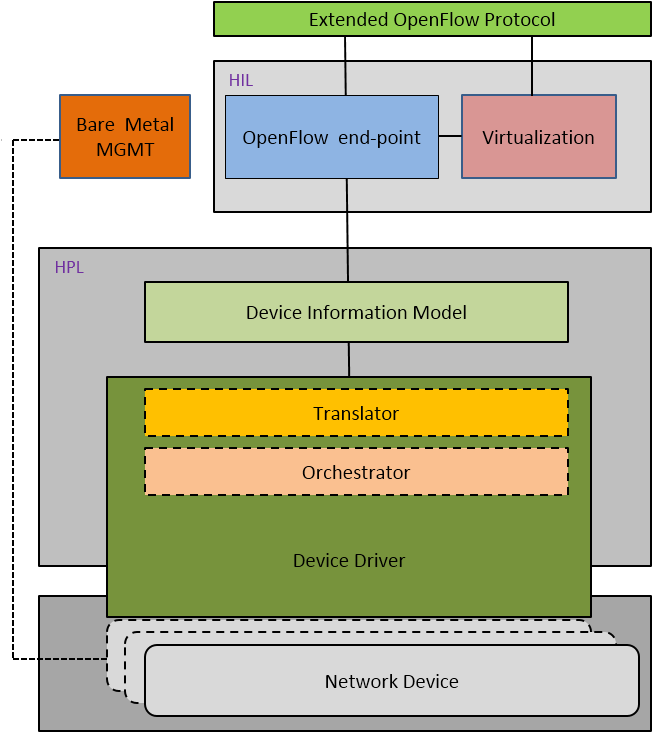
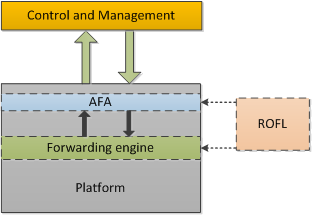
 During TNC2014 Conference in Dublin (19-22.05.2014) ALIEN will present Hardware Abstraction Layer for non-OpenFlow capable devices. Session Advanced networking is planned on Thuesday 20 May at 2 p.m.
During TNC2014 Conference in Dublin (19-22.05.2014) ALIEN will present Hardware Abstraction Layer for non-OpenFlow capable devices. Session Advanced networking is planned on Thuesday 20 May at 2 p.m.
“This presentation shows a way forward for adding SDN-based control on network devices that are not compatible with OpenFlow and introduces a Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) for non-OpenFlow capable devices that addresses this problem and discuss its advantages. In particular, the presentation explains how a HAL-based architecture can support different classes of network devices.”
Read More